Mastering Photo Metadata: A Guide to EXIF, IPTC, and XMP Data Standards
Ever wondered about the hidden story within every digital photo you take or see online? It's a layer of information, a digital fingerprint written in code. This data, known as metadata, holds the secrets to how, when, and where a photo was created. But have you ever wondered about the different types of this data? And more importantly, what is the best tool to view metadata? Understanding the distinctions between EXIF, IPTC, and XMP image metadata standards is the first step toward mastering your digital images, whether you're a professional photographer, a content creator, or simply curious.
This comprehensive guide will demystify these three core standards. We will explore what each one is, what information it holds, and why it matters. By the end, you'll know exactly how to access this rich information and use it to your advantage. If you're eager to see what's hiding in your own pictures, you can check photo details right now with a secure and private tool.

Understanding EXIF Data: Your Camera's Digital Fingerprint
When you press the shutter button, your camera does more than just capture a moment; it meticulously records a host of technical details. This is EXIF (Exchangeable Image File Format) data. Think of it as the photo's birth certificate, automatically generated by the camera or smartphone. It’s the most common type of metadata and is invaluable for analyzing the technical aspects of a photograph.
What Information Does EXIF Capture?
EXIF data is primarily about the "how" of a picture. It provides a detailed snapshot of the exact settings used to create the image. This information is a goldmine for anyone looking to understand or replicate a specific photographic style. Key data points include:
-
Camera Settings: Shutter speed, aperture, ISO speed, and focal length.
-
Device Information: The make and model of the camera or smartphone.
-
Date and Time: The exact moment the photo was taken.
-
GPS Location: Geographic coordinates pinpointing where the photo was shot (if enabled).
-
Flash Status: Whether the flash was used or not.
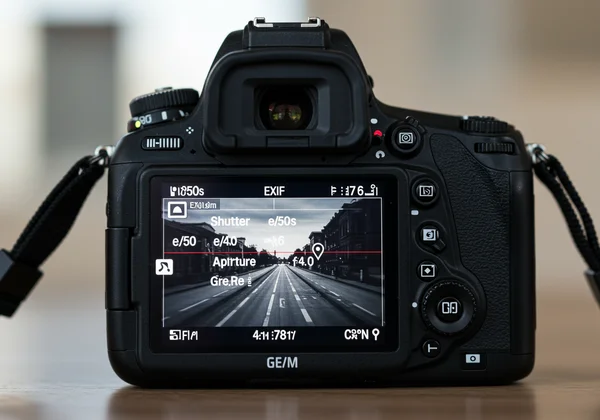

Practical Uses of EXIF Data for Photographers
For photographers, EXIF data is a powerful learning tool. By studying the EXIF of their own work or that of others, they can understand what settings lead to a desired outcome. Did a low-light shot turn out great? Check the ISO and aperture settings. Admire the motion blur in an action shot? The shutter speed in the EXIF data holds the answer. It’s also crucial for organizing photo libraries by date or camera model.
Diving into IPTC Metadata: Professional Photo Management & Copyright
While EXIF is about the camera, IPTC (International Press Telecommunications Council) metadata is about the content and the creator. Developed for photojournalists, this standard is essential for describing, organizing, and protecting images. If EXIF is the technical blueprint, IPTC is the photo's administrative file, containing crucial photo copyright info.
Core Information Within the IPTC Standard
IPTC focuses on descriptive and administrative details that help manage and distribute images professionally. It allows creators to embed their ownership and contact information directly into the file, which is vital for protecting intellectual property. Essential IPTC fields include:
-
Creator Details: The photographer's name, website, and contact information.
-
Copyright Notice: A clear statement of copyright ownership.
-
Keywords and Captions: Descriptive text and tags that make images searchable.
-
Headline and Description: A title and detailed summary of the image's content.
-
Location Information: City, state, and country where the photo was taken (manually entered).
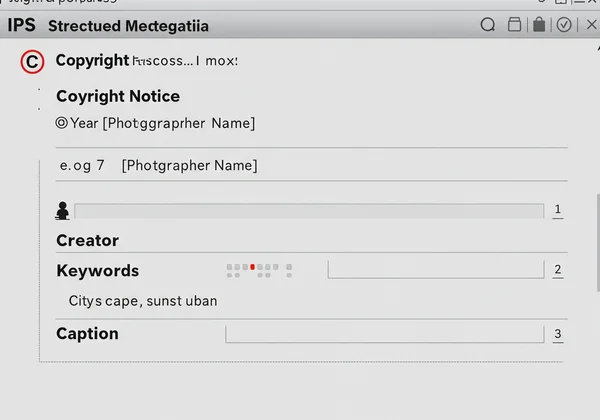
How IPTC Facilitates Photojournalism & Digital Asset Management
For news agencies, stock photo sites, and large organizations, IPTC is the backbone of their workflow. It allows editors to quickly find relevant images using keywords, identify the photographer, and access caption information. For any professional managing a large library of images, IPTC provides the tools for effective digital asset management, ensuring every photo is properly credited and easy to locate. You can easily inspect this data with a powerful photo metadata viewer.
Exploring XMP: The Flexible & Extensible Metadata Framework
XMP (Extensible Metadata Platform) is the most modern and flexible of the three standards. Developed by Adobe, it was designed to build upon and even incorporate EXIF and IPTC data into a unified, extensible format. Its key advantage is its structure, which can store a vast range of information and is not limited to a predefined set of fields.
XMP's Structure and Advantages for Digital Workflows
Unlike EXIF and IPTC, which have rigid structures, XMP is built on XML, allowing it to be easily extended with custom data fields. A major benefit is that XMP data is often stored in a "sidecar" file or within the image file itself in a way that allows for non-destructive edits. This means you can add or change editing information (like adjustments made in Lightroom) without altering the original image data. This flexibility is key to modern digital workflows.
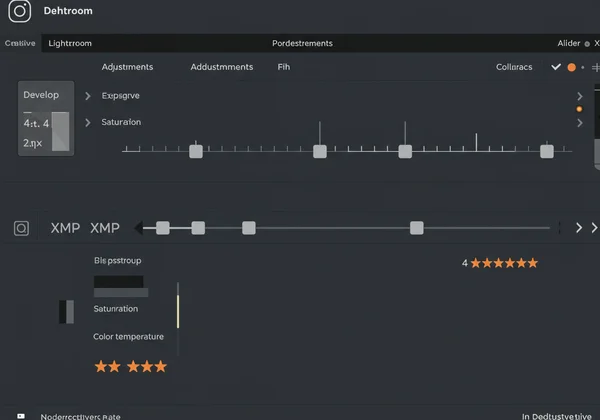
Common Applications of XMP in Creative Software
XMP is the standard used by Adobe Creative Cloud applications like Photoshop, Lightroom, and Bridge. When you rate a photo with stars, apply a label, or make develop adjustments in Lightroom, you are creating XMP data. This data travels with the image, ensuring that your edits, keywords, and ratings are preserved across different applications and systems, making it an indispensable tool for content creators.
EXIF vs. IPTC vs. XMP: Understanding the Key Differences & Overlaps
While these three standards all serve to enrich an image file, they have distinct purposes. A single image file can, and often does, contain all three. Understanding their relationship is crucial for effective photo management. Using a comprehensive online exif viewer is the best way to see them all side-by-side.
A Comparative Look: Purpose, Data Types, and Scope
- EXIF: Purpose: Technical data recording. Data: Camera settings, date/time, GPS. Scope: Automatically generated by the device at the time of capture.
- IPTC: Purpose: Descriptive and administrative data. Data: Copyright, creator info, keywords, captions. Scope: Manually added by the creator or an organization for management and licensing.
- XMP: Purpose: Flexible and extensible data storage. Data: Can contain EXIF, IPTC, edit history, ratings, and custom info. Scope: Both automatically generated by software and manually added by users.
Essentially, EXIF tells you what the camera did. IPTC tells you what the photo is about and who owns it. XMP can contain all of that information and much more, including the entire history of its edits.
When to Use Which: Choosing the Right Metadata Standard(s)
You don't typically "choose" one over the other; they work together. A professional photographer will rely on EXIF for technical analysis, embed IPTC data to protect their copyright and describe their work for clients, and use software that generates XMP to track their editing process. For the everyday user, being aware of EXIF, especially GPS data, is a critical privacy concern.
Viewing and Managing All Your Photo Metadata with Ease
With so much valuable—and sometimes sensitive—information packed into your photos, having a reliable way to view it is essential. An image metadata viewer is the perfect tool for this job, allowing you to unlock the full story behind any picture.
Why Online Metadata Viewers are Essential
Desktop software can be cumbersome and expensive. An online tool offers instant access without any installation. It allows you to quickly check any image file from any device, whether you're a photographer double-checking client work, a social media user wanting to strip exif data before sharing, or a blogger optimizing images for your website.
Instantly Access EXIF, IPTC, and XMP Securely
The best tools prioritize not only functionality but also your privacy. This free online EXIF reader is designed with ultimate security in mind. Its core advantage is that all processing happens directly in your browser. Your images are never uploaded to a server, meaning your private photos and their location data remain completely confidential on your own device.
With support for a wide range of formats, including HEIC, our platform provides a clear, structured view of all three metadata standards—EXIF, IPTC, and XMP. It’s the simplest and most secure way to view image exif data.
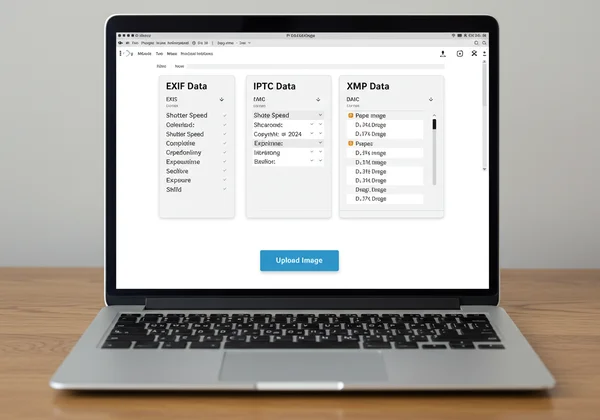
Mastering Metadata: Empowering Your Digital Photos
This knowledge empowers you to improve your photography, protect your work, manage your digital assets, and safeguard your privacy. Each standard tells a different part of your photo's story, from its technical creation to its creative journey.
Ready to uncover the hidden data in your own images? Try our free tool today and instantly reveal the complete metadata of your photos, all securely and privately.
Common Questions About Image Metadata Standards
What is the main difference between EXIF and IPTC metadata?
The primary difference lies in their purpose. EXIF data is technical information automatically recorded by your camera (shutter speed, ISO, GPS). IPTC metadata is descriptive and administrative information that you or an organization adds manually (copyright, keywords, creator name).
Do all image file formats contain EXIF, IPTC, or XMP?
Not all. JPEGs and TIFFs almost always support all three. Formats like PNG have more limited native support but can contain metadata within an XMP block. RAW files contain extensive manufacturer-specific EXIF data. To be sure what a file contains, it's best to use a comprehensive image metadata viewer.
How can I view the complete metadata of my photos securely online?
The most secure way is to use a tool that processes images locally in your browser. Our online tool is designed for this purpose; it allows you to view full EXIF, IPTC, and XMP data without ever uploading your file to a server, ensuring your privacy is completely protected.
Can metadata be edited or removed from my digital images?
Yes. While some data like basic camera settings are difficult to change, most metadata can be edited or removed (stripped). This is often done to protect privacy by removing GPS coordinates or to reduce file size for websites.
What is the best online tool to view all types of image metadata?
The best tool is one that is comprehensive, user-friendly, and prioritizes your privacy. This online viewer excels in all three areas by supporting EXIF, IPTC, and XMP across many file types and guaranteeing security with its browser-side processing. You can check exif data instantly and safely.