Professional RAW EXIF Data Management: A Photographer's Guide
As a professional photographer, your RAW files are the digital negatives of your art. They hold every piece of data captured by your camera's sensor, offering unparalleled flexibility in post-processing. But hidden within these powerful files is a vast amount of EXIF data—a detailed record of your camera settings, location, and more. How can you manage this data effectively to improve your workflow and protect client privacy?
Ready to take control of your RAW EXIF workflow? This guide shows you exactly how. We'll explore what makes RAW metadata unique, how to preserve it during editing, and why a privacy-first approach is essential when sharing files. We'll also show you how a secure, browser-based tool can simplify the entire process. For a quick and safe way to inspect your files, you can check your photos right now without uploading anything.
Understanding RAW File EXIF Data: A Metadata Viewer's Guide
Before you can manage your RAW file EXIF data, it's crucial to understand why it's different from the metadata in JPEGs or other compressed formats. RAW files are not just images; they are comprehensive data packages straight from your camera's sensor, and their metadata reflects this richness.
This unprocessed information gives you maximum control but also means the EXIF data is more complex and detailed. Understanding this data is the first step toward a professional workflow.
What Makes RAW Files Unique in Metadata Capture
When you shoot in JPEG, your camera processes the sensor data, applies settings like white balance and sharpness, and compresses it into a final image. During this process, some of the original sensor metadata can be simplified or discarded.
RAW files store unprocessed sensor data with extensive metadata. This includes standard EXIF tags like shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. It also contains proprietary information from manufacturers called "MakerNotes." This deeper level of metadata capture provides a complete picture of the exact conditions and settings at the moment of capture, which is invaluable for technical analysis and advanced editing.
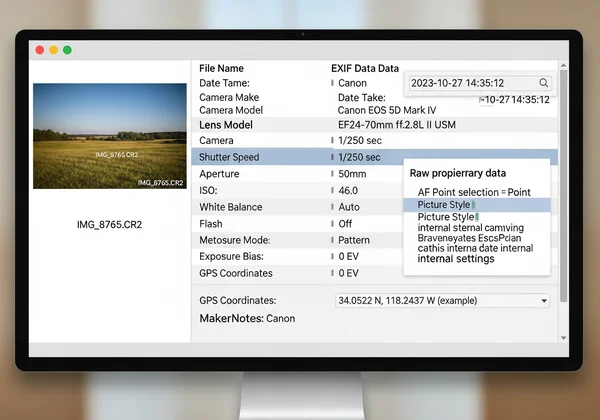
Decoding Manufacturer-Specific EXIF in CR2, NEF, and ARW Files
Every camera manufacturer has its own proprietary RAW format. Canon uses .CR2 or .CR3, Nikon uses .NEF, and Sony uses .ARW. While they all contain standard EXIF data, they also include unique MakerNotes that only specific software can read.
Manufacturer-specific data reveals lens details, autofocus points, dynamic range settings, and camera temperature. For photographers, this information helps understand equipment performance in various conditions. A powerful viewer is needed to decode these specific tags and present them in a readable format, helping you analyze your work with precision.
Professional Photo Metadata Preservation: Best Practices
Your professional photo metadata is a valuable asset. It serves as a record of your technical decisions and creative process. Losing this data during your workflow is like tearing out pages from your notebook—the core information might still be there, but the crucial context is gone.
Implementing robust preservation techniques ensures that this data remains intact from the moment you press the shutter to the final delivery of your images. This protects the integrity of your work and provides a consistent record for future reference.
Maintaining EXIF Integrity During Post-Processing
Your post-processing software, whether it's Adobe Lightroom, Capture One, or something else, is where your RAW files come to life. However, this is also where metadata can be accidentally altered or stripped. When you edit a RAW file, the software often creates a "sidecar" file (like a .XMP file) to store your changes without modifying the original RAW data.
To maintain integrity, ensure your software is configured to read, write, and preserve all metadata. Be mindful when exporting files to other formats like JPEG or TIFF. Check your export settings to ensure all necessary EXIF and IPTC (copyright) data is carried over. A consistent workflow prevents valuable information from being lost in translation between file formats.
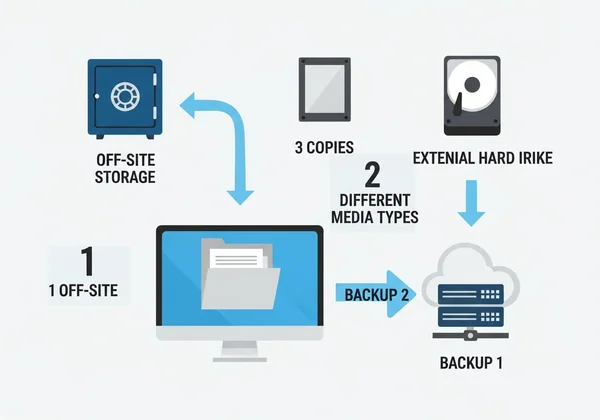
Backup Strategies for Critical Camera Settings Data
Losing your RAW files is a photographer's worst nightmare, and losing their associated metadata is a close second. A solid backup strategy is non-negotiable for metadata preservation. Your backup strategy must include RAW files and sidecar files with edits.
Follow the 3-2-1 rule:
- Three copies of your data.
- On two different media types (e.g., an external hard drive and a network-attached storage device).
- With one copy stored off-site (e.g., a cloud service or a drive at a different physical location).
This ensures that no matter what happens—hard drive failure, theft, or disaster—your complete creative record, including all critical camera settings data, is safe and recoverable.
Privacy-First Approach to Client Photo Metadata
As a professional, you handle sensitive images for your clients. Weddings, family portraits, and corporate events all come with an expectation of privacy. The EXIF data embedded in these photos can contain sensitive information, and managing it responsibly is a core part of professional ethics and building client trust.
Adopting a privacy in photography mindset means being aware of what data your files contain and having a secure method to inspect and manage it before delivery. This protects your clients and your professional reputation.
Sensitive Information in Client RAW Files: What to Watch For
While camera settings are generally harmless, other EXIF tags can pose a significant privacy risk. GPS data is the primary privacy concern. When your camera's GPS is enabled, every photo contains precise location coordinates. For a private family session at their home, this creates a significant privacy risk.
Other potentially sensitive data includes the exact date and time of the shoot and the camera's serial number, which could be used to trace equipment. Before sending any files to a client or a third-party vendor, you must inspect them for this information and decide what needs to be removed. You can quickly view image metadata to see exactly what your files contain.

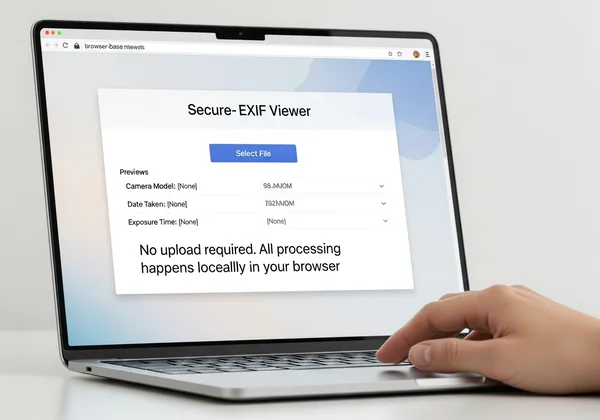
Secure Client Metadata Transfer Without Server Upload
When you need to check a client's RAW file for sensitive metadata, where do you turn? Many online tools require you to upload your images to their servers for processing. For a professional handling confidential client work, this is an unacceptable risk. Uploading a high-resolution RAW file to an unknown server exposes it to potential data breaches, unauthorized use, or theft.
The solution is to use a tool that works entirely within your browser. Our online EXIF viewer is built on this privacy-first principle. When you select a file, all the analysis happens locally on your computer. Your photo never leaves your device and is never sent over the internet. This provides a completely secure way to inspect metadata, giving you peace of mind when handling sensitive client files.
Implementing Your Professional RAW EXIF Workflow
As a professional photographer, managing your RAW EXIF data isn't optional—it's essential to protecting your work and your clients' privacy. Understanding the richness of RAW metadata helps you refine your technique, while actively preserving it maintains the integrity of your creative process. Most importantly, adopting a privacy-first approach protects your clients and solidifies your reputation as a trustworthy professional.
Implement these practices in your photography workflow:
- Understand Your Data: Recognize that RAW files contain extensive metadata, including manufacturer-specific MakerNotes that offer deep technical insights.
- Preserve Integrity: Implement careful post-processing habits and robust backup strategies to ensure your valuable EXIF data is never lost.
- Prioritize Privacy: Always inspect client photos for sensitive information like GPS coordinates before delivery, using a secure, local-first method.
Ready to take control of your metadata? Use a tool that respects your privacy and professional needs. Try our free tool to instantly and securely analyze your RAW file EXIF data without ever uploading a single file.
Frequently Asked Questions About RAW EXIF Data
Do RAW files contain more EXIF data than JPEG files?
Yes, absolutely. RAW files contain the full, unaltered data dump from the camera's sensor, including detailed manufacturer-specific information (MakerNotes) that is often simplified or removed when a camera creates a compressed JPEG file. This makes RAW files much richer in technical detail.
How can I check if my RAW file metadata is intact?
The best way is to use a reliable metadata viewer. While your editing software shows some data, a dedicated tool can provide a more comprehensive view. A browser-based solution like our EXIF viewer allows you to quickly inspect a RAW file (or its exported version) to see if all expected fields, from camera settings to copyright info, are present and correct.
Is it safe to send RAW files with EXIF data to clients?
It depends on what data is present. Sending files with technical settings like aperture and ISO is generally safe. However, you should always check for and remove sensitive information like GPS location data before sending files to clients. This protects their privacy and is a mark of professional responsibility.
Can I edit EXIF data in RAW files without losing image quality?
Yes. Editing EXIF data does not affect the image sensor data itself, so it does not degrade image quality. Most professional editing software edits metadata non-destructively, often by writing changes to a .XMP sidecar file, leaving the original RAW file untouched. This allows you to modify or add copyright information without any risk to your image. You can always verify the data before and after editing.